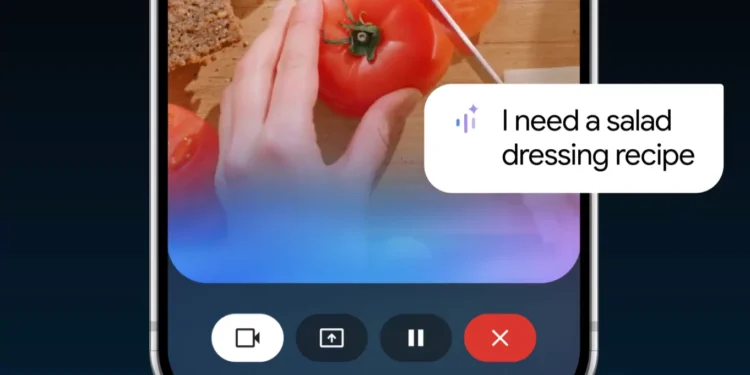
Imagine pointing your phone at a restaurant’s storefront and instantly seeing reviews, menu highlights, and peak hours without typing a word. Or scanning an unfamiliar plant and immediately learning how to care for it. Google’s latest innovation real time AI camera sharing integrated directly into Search is about to make these scenarios an everyday reality, fundamentally changing how we interact with the world around us.
What Is Google’s Real-Time AI Camera Search?
Google is elevating visual search by integrating live camera feeds directly into its search interface. Unlike previous visual search tools that required taking a photo first, this new feature allows users to simply point their camera at objects, places, or text in real-time, with AI instantly analyzing and delivering relevant information overlaid on the camera view.
This represents a significant evolution from Google Lens, which already allowed users to search with images but required a more deliberate, multi-step process. The new integration creates a seamless, continuous search experience that blends the physical and digital worlds more naturally than ever before.
The technology combines several advanced AI systems working simultaneously:
- Real-time object recognition
- Spatial awareness and context understanding
- Text recognition and translation
- Knowledge graph integration for instant information retrieval
How The New Camera Search Feature Works
Using the feature is designed to be intuitive and frictionless:
- Open the Gemini app
- Tap the new camera icon in the search bar
- Point your camera at whatever you want to learn about
- Watch as information appears directly on your screen, contextually placed near relevant objects
Behind this simple interface lies complex technology. The system processes camera data locally on your device for initial object detection, then sends anonymized data to Google’s servers for deeper analysis and information retrieval. This split approach helps balance performance with privacy while maintaining speed.
The system can recognize and provide information about:
- Products and shopping items with price comparisons
- Landmarks and buildings with historical information
- Plants and animals with identification and facts
- Food dishes with nutritional information and recipes
- Text in multiple languages with instant translation
Practical Applications for Everyday Users
This technology transforms mundane daily activities into opportunities for discovery:
Shopping: Point your camera at products in-store to see online prices, reviews, and alternatives instantly. For clothing, the system can even suggest outfit pairings or show how items look on different body types.
Travel: Scan buildings, landmarks, or neighborhoods for historical information, points of interest, and insider tips without constantly referencing a guidebook or stopping to type searches.
Education: Students can aim their cameras at textbook problems for step-by-step solution guidance, or scan natural objects for instant educational content about geology, biology, and more.
Cooking: Identify ingredients at the grocery store, see nutritional information for prepared foods, or get recipe suggestions by scanning what’s already in your refrigerator.
Accessibility: For those with reading difficulties or in foreign countries, the real-time text recognition and translation features remove significant barriers to understanding written information.
Privacy and Data Considerations
Google has emphasized privacy protections in this new feature, likely anticipating concerns about a constantly watching camera:
- Processing happens on-device when possible
- Users can enable an “ephemeral mode” where no images are stored
- Clear visual indicators show when the camera is actively analyzing
- Granular permissions allow users to limit what types of recognition are active
- Option to automatically blur faces and license plates
However, questions remain about data retention policies for server-processed images and how the data might be used to train future AI models. Google states that while anonymous data may help improve the service, users can delete their visual search history through their Google account settings.
Compared to competitors like Amazon’s visual search (primarily focused on shopping) or Snapchat’s visual search (emphasizing social contexts), Google’s implementation offers more comprehensive information but potentially collects more varied data in the process.
Future Implications for Search Technology
This technology represents a significant step toward ambient computing—where technology fades into the background while providing contextual information without explicit commands.
For Google, real-time visual search serves multiple strategic purposes:
- Maintaining search dominance as user behavior shifts from text to visual queries
- Collecting valuable real-world imagery to improve their AI systems
- Creating new advertising opportunities through suggested products and services
- Establishing a platform for future AR (augmented reality) applications
This could eventually evolve into AR glasses or other wearables that provide continuous information about your surroundings without requiring you to hold a phone. Google’s previous experiments with Google Glass were perhaps too early, but this mobile implementation may help normalize the concept.
For competing platforms, this raises the stakes in the visual search arena. Apple has been rumored to be developing similar capabilities, while Meta continues building out its own visual understanding technologies primarily for social contexts.
Key Takeaways
- Google’s real-time AI camera search creates a more intuitive, seamless way to discover information about the world around you
- The technology combines object recognition, text analysis, and Google’s knowledge graph for instant contextual information
- Initial rollout focuses on newer smartphones with plans to expand to more devices
- Practical applications span shopping, travel, education, and accessibility
- Privacy protections include on-device processing and ephemeral modes, though some data will still reach Google’s servers
- This represents a significant step toward ambient computing and potential future AR applications
Conclusion
Google’s integration of real-time AI camera capabilities directly into Search represents one of the most significant evolutions in search technology since voice queries. By removing friction between curiosity and information, this feature fundamentally changes how we can interact with both the physical and digital worlds.
While the technology offers tremendous convenience and new possibilities, users should remain mindful of the privacy implications of a more camera-centric search experience. As with most technological advances, the true impact will be determined by how people actually incorporate it into their daily lives and what boundaries they set.
Have you had a chance to try Google’s new camera search feature? What would you most likely use it for in your daily life? Share your thoughts in the comments below, or subscribe to our newsletter for more analysis of cutting-edge tech developments.